Scabies
Left untreated, scabies can lead to secondary bacterial infections due to excessive scratching. The condition can affect individuals of all ages, but it is particularly prevalent in settings such as nursing homes, childcare facilities, and dormitories.
At Pinnacle Dermatology, our experienced dermatologists can diagnose scabies through clinical examination or skin scrapings, ensuring an accurate diagnosis. We provide individualized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs, which typically include prescribed topical or oral medications to eradicate the mites and alleviate symptoms.
Scheduling an online appointment with one of our trusted skin experts is crucial to gain relief from symptoms and prevent the spread of the infestation. Trust Pinnacle Dermatology to help you achieve healthy, itch-free skin and ensure a complete recovery.
Examples of Scabies
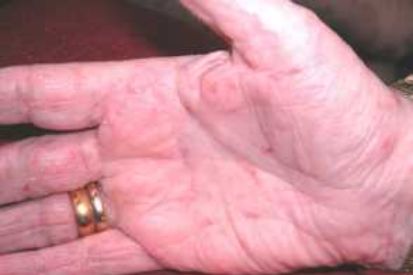
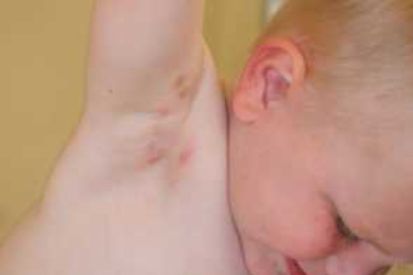
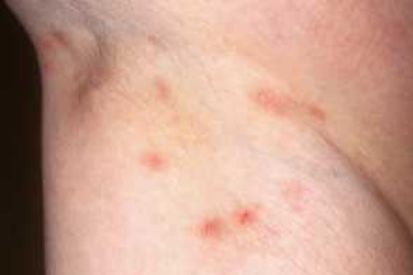
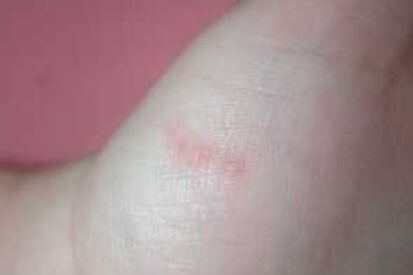
What are the Symptoms of Scabies?
- Intense itching, especially at night.
- As the scabies mites burrow into the skin and lay eggs, they cause a rash that appears as tiny red bumps or pimples.
- The rash may develop into more crusty or scaly areas.
- The itching is a result of the body's allergic reaction to the presence of the mites and their waste.
Causes of Scabies
- Scabies is caused by an infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite.
- These tiny mites are microscopic and cannot be seen by the naked eye.
- The mites burrow into the outer layers of human skin to live and lay their eggs, triggering an allergic reaction in the host.
- Scabies is highly contagious and can spread through close personal contact with an infected person.
How to Prevent Scabies
If someone in close contact has scabies, seek prompt treatment for everyone involved to prevent the mites from spreading.
Scabies FAQs
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by tiny mites. It's often transmitted through close personal contact, and you may have picked it up from someone who has scabies.
Yes, scabies is contagious. It can spread through prolonged skin-to-skin contact. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent further transmission to family members or close contacts.
Dermatologists often diagnose scabies by examining the rash and may use a microscope to identify the mites, eggs, or fecal matter. Clinical expertise allows them to distinguish scabies from other skin conditions.
Absolutely. Dermatologists may recommend anti-itch creams or antihistamines to alleviate itching during the treatment period. They can provide guidance on managing discomfort and promoting healing.
Dermatologists will advise on suitable skincare products during scabies treatment. It's crucial to inform them about any products you plan to use to ensure they won't interfere with the prescribed medications or exacerbate the condition.
How to Treat Scabies
- Topical Medication to eliminate the mites.
- Oral Ivermectin on select cases.
- Oral Antihistamines to reduce itching.
- Topical Steroids to reduce itching.
- Systemic Steroids in severe cases to reduce itching.
Featured Blogs

- General Dermatology
- Skin Care
- Chronic Skin Conditions
We asked one of our skin care professionals for tips on how to clear up acne. Here's what he had to say.
Read More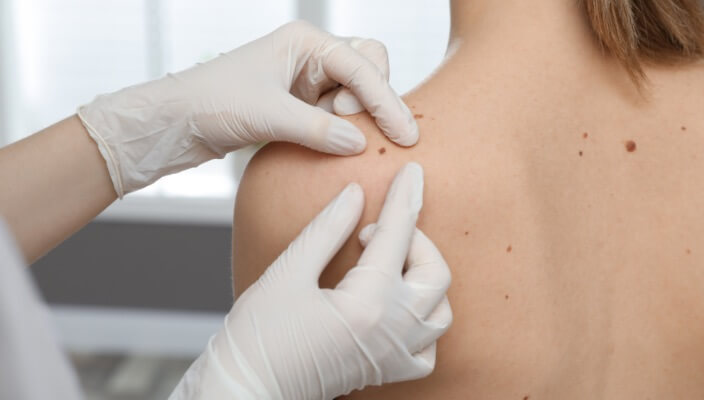
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Navigating the landscape of Total Body Skin Exams: Uncover the comprehensive process, understand why it matters for skin health, and gain insights into what to expect during these essential dermatological examinations.
Read More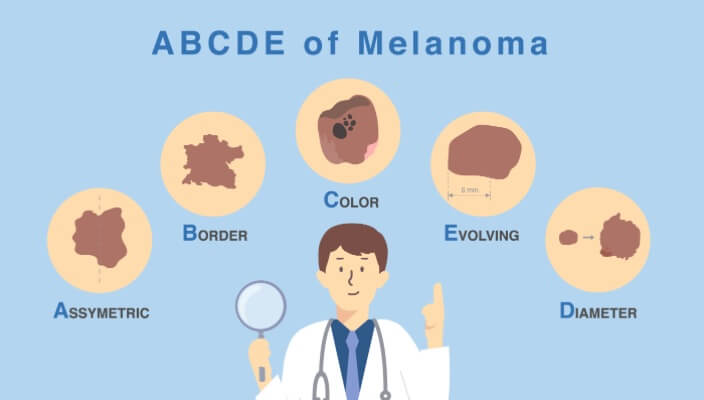
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Learn the ABCDEs of Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
Read MoreFeatured Products

CLn BodyWash
CLn BodyWash is designed for infection- and eczema-prone skin. It is an effective cleanser that is tough on the microbes but gentle on skin. Designed for skin prone to infection, irritation, dermatitis, redness, folliculitis, acne, eczema and compromised skin. 12 fl oz / 354 mL

CLn HandWash
Designed by dermatologists, this non-prescription cleanser is tough on microbes but easy on the skin. It can be used for frequent hand washing that can cause sensitive skin to over dry and crack. Openings in the skin lead to increased risk of infection. CLn HandWash is preserved with sodium hypochlorite, but includes glycerin so it can be used daily without irritation or dryin. 12 fl oz


