Chicken Pox
After the initial infection, the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the body's nerve tissues. In some cases, particularly in older adults or those with weakened immune systems, the virus can reactivate later in life, leading to a painful condition known as shingles (herpes zoster).
Managing Chickenpox and Shingles
If you or your child exhibit symptoms of chickenpox, it is crucial to seek medical advice promptly. Contact your general practitioner, pediatrician, or an infectious disease specialist to confirm the diagnosis and receive appropriate care. Early intervention can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
At Pinnacle Dermatology, our skin experts specialize in addressing the dermatological impacts of chickenpox. We can develop a personalized treatment plan to manage scarring and other skin-related issues during the recovery phase, ensuring comprehensive care tailored to your needs. Our goal is to support your healing process and help restore healthy, clear skin.Examples of Chicken Pox
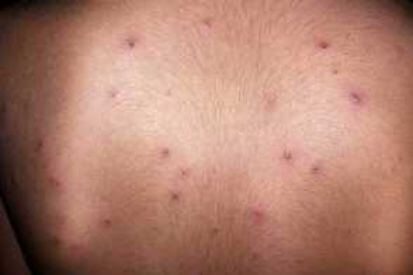
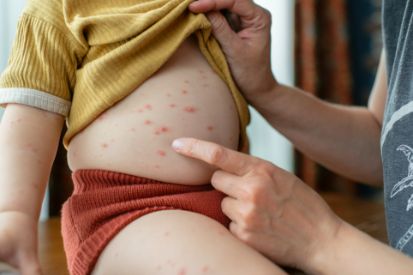
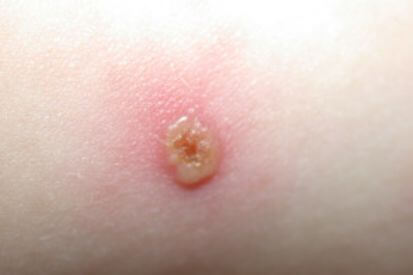
What are the Symptoms of Chickenpox?
- Rash: Itchy rash or red spots on the face, chest, and back before spreading to other parts of the body.
- Fever: Many individuals with chickenpox develop a moderate to high fever.
- Fatigue.
- Headache: Headaches may occur.
- Loss of Appetite: People with chickenpox may have a reduced desire to eat.
- Sore Throat: A mild sore throat can occur.
Causes of Chickenpox
- Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV).
- It is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets from infected individuals.
- Direct contact with the fluid from chickenpox blisters can also transmit the virus.
- The virus can be airborne, making it easily transmissible in crowded environments.
How to Prevent Chickenpox
Chicken Pox FAQs
Yes, chickenpox can cause scarring, particularly if the blisters are not properly cared for. While the blisters from chickenpox can leave temporary scars, these can often be minimized with the right precautions and care.
Preventing Chickenpox Scars
To reduce the risk of scarring, it is crucial to avoid scratching the blisters. Scratching can lead to infection and increase the likelihood of permanent scars. Here are some steps to help manage chickenpox blisters and prevent scarring:
- Keep Nails Short and Clean: This reduces the damage that scratching can cause if it happens unintentionally.
- Use Topical Treatments: Calamine lotion or over-the-counter anti-itch creams can help soothe the skin and reduce the urge to scratch.
- Apply Cool Compresses: Cool, wet cloths applied to the blisters can provide relief from itching.
- Take Antihistamines: Over-the-counter antihistamines can also help control itching.
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Keep the skin clean to prevent secondary infections, which can exacerbate scarring.
Healing Process
Once the blisters crust over and begin to heal, the risk of scarring significantly decreases. The crusts should fall off naturally, revealing new skin underneath. It's important not to pick at the crusts, as this can interfere with the healing process and increase the chance of scarring.
Post-Infection Care
After the chickenpox blisters have healed, some people may still be concerned about residual marks or scars. In such cases, dermatological treatments can help. Pinnacle Dermatology offers specialized care to address any lingering skin issues, such as:
- Moisturizers and Healing Ointments: These can help the skin repair itself more effectively.
- Scar Treatments: Options like silicone gels, sheets, or dermatological procedures can reduce the appearance of scars.
- Professional Dermatological Care: Our experts can provide personalized treatment plans to address scarring and promote healthy skin regeneration.
By following these guidelines and seeking appropriate care, you can minimize the risk of scarring from chickenpox and support the skin’s healing process.
Seeing a dermatologist for chickenpox is not typically necessary for managing the primary symptoms of the illness, such as the characteristic itchy red spots or blisters. These can usually be effectively managed with the care of a general practitioner or pediatrician. However, consulting a dermatologist can be beneficial if you experience complications, severe symptoms, or if you have concerns about scarring and skin care during the healing process. A dermatologist can provide specialized treatments and advice to help prevent long-term skin issues and ensure optimal recovery.
For individuals at higher risk of severe complications, such as those with weakened immune systems, pregnant women, or adults who have not previously contracted chickenpox, seeking a dermatologist’s expertise can be particularly advantageous. Additionally, if you notice signs of secondary infections, such as increased redness, pus, or severe pain around the blisters, it is important to seek dermatological advice. Dermatologists at Pinnacle Dermatology can develop personalized treatment plans to manage scarring, minimize itching, and address any skin-related concerns during the recovery phase, ensuring comprehensive care tailored to your specific needs.
Relieving the itching associated with chickenpox can significantly improve comfort and prevent complications. Here are several effective strategies to manage itching during a chickenpox infection:
Cool Baths: Taking cool baths can soothe the skin and reduce itching. Adding baking soda, colloidal oatmeal, or uncooked oatmeal to the bathwater enhances the soothing effect. Soaking in these baths for 15-20 minutes several times a day can provide relief.
Calamine Lotion: Applying calamine lotion to the affected areas can help alleviate itching. This over-the-counter remedy has a cooling effect and can reduce irritation when applied gently to the blisters.
Loose, Lightweight Clothing: Wearing loose, lightweight clothing made of soft, natural fabrics like cotton can help avoid further irritation of the skin. Tight or rough fabrics can exacerbate itching and discomfort.
Over-the-Counter Antihistamines: Taking over-the-counter antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl), can help reduce itching. It's essential to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially for children, to ensure proper dosing and safety.
Topical Anti-Itch Creams: In addition to calamine lotion, over-the-counter anti-itch creams containing ingredients like pramoxine or hydrocortisone can provide additional relief. These should be used as directed to avoid over-application and potential side effects.
Maintaining Short, Clean Nails: Keeping fingernails short and clean can reduce the risk of skin damage from scratching. For young children, wearing mittens or socks over their hands at night can prevent scratching during sleep.
It is crucial to avoid scratching the blisters, as this can lead to secondary infections and increase the risk of scarring. Employing these strategies can help manage itching effectively and support the healing process during a chickenpox infection.
How do you Treat Chickenpox?
While dermatologists primarily specialize in skin conditions, they may not be the first line of care for chickenpox. General practitioners, pediatricians, or infectious disease specialists often manage chickenpox cases. However, if complications arise, or if there are concerns about scarring or skin-related issues during the recovery phase, one of our dermatologists may become involved in the treatment plan.
Featured Blogs
- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
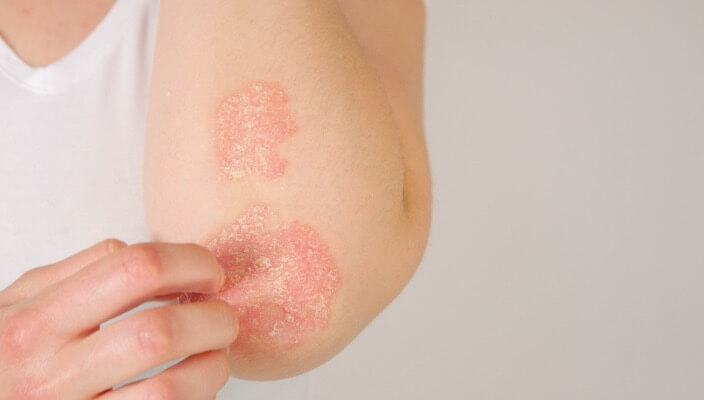
Explore effective coping strategies and management techniques for psoriasis, tailored to individual needs and guided by dermatological expertise.
Read More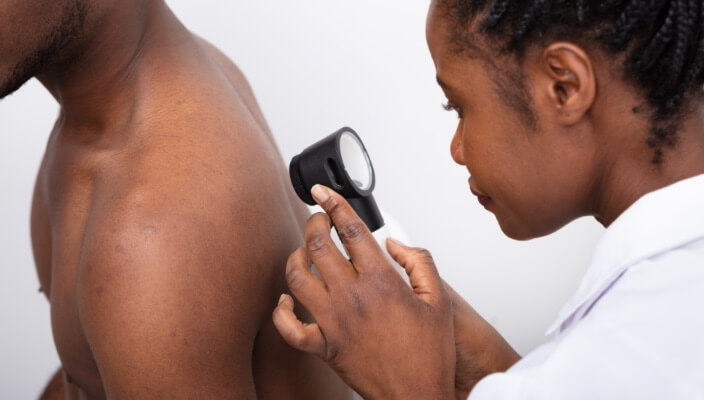
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
Total Body Skin Exams (TBSEs) are crucial for healthy skin. Learn more about the importance of TBSEs and skin cancer detection.
Read More
- General Dermatology
Curious if it's time to consult a dermatologist? Explore key signs and considerations to determine whether a visit to a skincare expert is essential for your skin health and well-being.
Read MoreFeatured Products
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!


