Genital Warts
If you notice any symptoms of genital warts, it is crucial to seek professional medical advice. At Pinnacle Dermatology, our skilled dermatologists provide expert diagnosis and a range of treatment options tailored to the specific needs of each patient. Treatment methods vary depending on the size, number, and location of the warts and may include topical medications, cryotherapy, surgical removal, or other advanced dermatological procedures.
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital in managing genital warts effectively and preventing further spread of the infection. Contact Pinnacle Dermatology today to schedule a consultation and discuss the best treatment plan for your condition.
Examples of Genital Warts
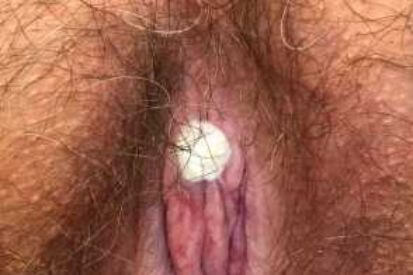
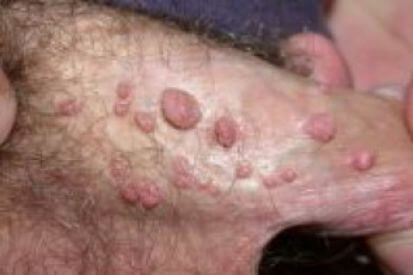
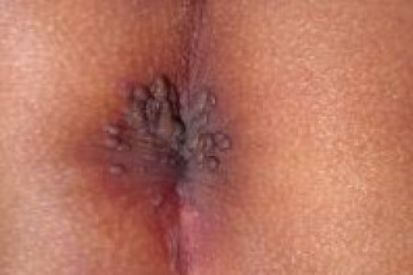

Warning
This content contains sensitive images.
Symptoms of Genital Warts?
- Bleeding during intercourse and/or itching in the genital area.
- Small, roundish, bumpy, and rough growths.
- In men, often appear on the penis, scrotum, and anus.
- In women, found on the vulva, vaginal walls, and around anus or cervix.
Causes of Genital Warts
- Genital warts are primarily caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is a sexually transmitted infection.
How to Prevent Genital Warts
Preventing genital warts primarily involves strategies to reduce the risk of contracting the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is the underlying cause of genital warts. Here are some key preventive measures:
- Vaccination:
- Safe Sexual Practices:
- Regular Health Check-ups
- Know Your Partner's Sexual Health
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
FAQs for Genital Warts
While dermatologists are specialists in skin conditions and can provide effective diagnosis and treatment for genital warts, the first line of defense for this condition often involves primary care providers or healthcare professionals specializing in sexual health. Many individuals initially consult with their primary care physician, gynecologist (for women), urologist (for men), or another healthcare provider for an evaluation.
These healthcare professionals are trained to diagnose and manage a wide range of health issues, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like genital warts. They can conduct an initial examination, discuss symptoms, and recommend appropriate testing or treatment. In some instances, primary care providers may initiate treatment for genital warts, such as prescribing topical medications or performing minor procedures.
However, if the case is complex, the warts are extensive, or if there is a need for specialized treatment options, a referral to a dermatologist may be necessary. Dermatologists play a crucial role in managing skin conditions, and their expertise can be invaluable for more challenging cases of genital warts. They have access to advanced treatment methods, such as cryotherapy (freezing the warts), laser therapy, or surgical removal, which may be required for more persistent or severe cases.
Genital warts are a common sexually transmitted infection characterized by their distinctive appearance. They often present as small, raised growths that may be flesh-colored or grayish. The texture of these warts can vary; some may be flat, while others have a bumpy, cauliflower-like texture.
Here are some key characteristics to help you recognize genital warts:
- Color and Size: Genital warts are typically flesh-colored or gray. They can be very small and may cluster together to form larger growths.
- Texture: They can be flat or raised, with some having a rough, bumpy surface resembling cauliflower.
- Location in Men: In men, genital warts commonly appear on the penis, scrotum, groin, thighs, inside or around the anus, and sometimes the urethra.
- Location in Women: In women, they can be found on the vulva, vaginal walls, cervix, groin, thighs, and around or inside the anus.
- Other Areas: Less commonly, genital warts may also develop in the mouth or throat after oral sexual contact with an infected partner.
If you notice any unusual growths, bumps, or changes in the genital area, it is important to seek medical advice. A dermatologist or healthcare provider specializing in sexual health can perform a thorough examination to determine if these growths are genital warts. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms, preventing the spread of the infection, and reducing the risk of complications.
Remember, not all growths in the genital area are warts, so professional evaluation is essential to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Dermatologists offer various treatments for genital warts, depending on their size, location, and number. Options include:
- Topical Medications: Creams like Imiquimod, Podofilox, and Sinecatechins that help eliminate warts.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen.
- Laser Therapy: Using a focused beam to destroy wart tissue.
- Surgical Removal: Techniques like excision, electrosurgery, and curettage to remove warts.
A dermatologist will discuss these options, considering individual preferences and concerns, to create a personalized treatment plan. Follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor progress and manage any recurrences.
Yes, the HPV vaccine is crucial for preventing genital warts. It targets specific HPV strains that cause these warts and reduces the risk of infection.
Benefits of the HPV Vaccine:
- Prevention: Reduces the risk of contracting HPV strains that cause genital warts.
- Effectiveness: Provides long-term protection against targeted HPV strains.
Dermatologist Recommendations:
Dermatologists recommend the HPV vaccine and can provide information on:
- Eligibility: Who should get vaccinated.
- Dosage: Number and timing of doses.
- Overall Effectiveness: How well the vaccine prevents genital warts.
Treatment for Genital Warts
Genital Warts can be treated using a variety of techniques, some of which include:
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy).
- Electrocautery, which burns off the lesions.
- Prescription Medications.
Featured Blogs

- General Dermatology
- Skin Care
Acne can persist into adulthood, affecting individuals well beyond their adolescent years. Explore tips for managing your adult acne.
Read More
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Explore our comprehensive guide to gain insights into accurate diagnosis and expert care for chronic skin conditions.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Your skin is your largest organ and its first line of defense. Learn more about why a skin exam should be a part of your wellness routine.
Read MoreFeatured Products

SkinMedica AHA BHA Exfoliating Cleanser
This elegantly formulated exfoliating cleanser gently scrubs away dead skin, improving the appearance of skin tone and texture. Appropriate for all skin types. 6 fl oz / 177.4 g

SkinMedica Replenish Hydrating Cream
Hydrating Cream that hydrates as well as refreshes, soothes and nourishes sensitive skin. Appropriate for all skin types. 2 oz / 56.7 g


