Cellulitis
Recognizing the symptoms of cellulitis early is essential. If you notice swelling, redness, and tenderness, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. At Pinnacle Dermatology, our expert dermatologists are dedicated to providing you with the best care for healthy skin. We offer customized treatment plans to effectively combat cellulitis, helping you regain confidence in your skin.
Visit Pinnacle Dermatology for professional care and personalized treatment solutions.
Examples of Cellulitis
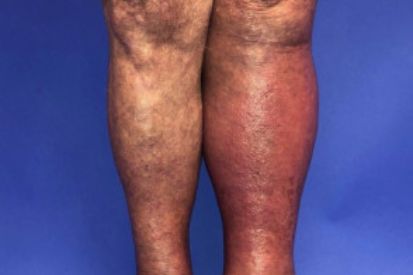
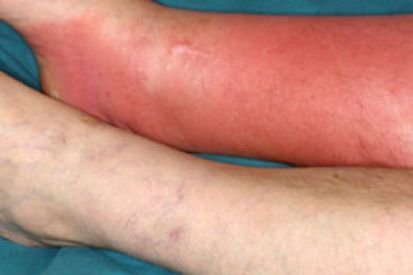
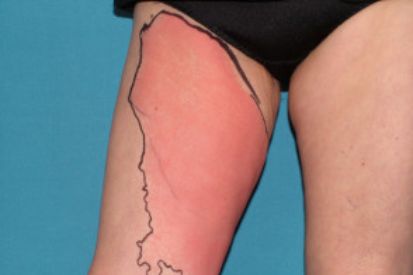
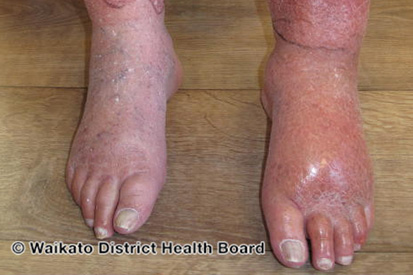
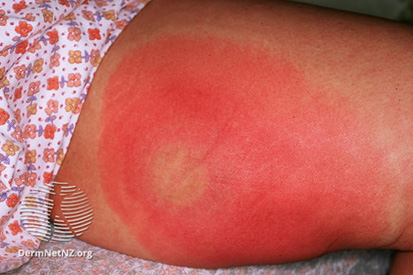
What are the Symptoms of Cellulitis?
- Redness: Skin appears red.
- Swelling: Swelling, can feel tight and warm.
- Pain or Tenderness: Infected area may be painful or tender.
- Warmth: Skin around the infection may feel warmer.
- Fever: May develop a fever.
- Red Spots or Blisters: Formation of red spots or blisters.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Swollen and tender lymph nodes.
- Pus or Drainage: Pus or other drainage from the affected area.
Causes of Celulitis
- Cellulitis is caused by either Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria.
- A break or cut in the skin causes the bacteria to enter the body, which leads to an active infection.
- Cracking or peeling skin between the toes.
- Insect bites or stings.
Cellulitis Prevention
Cellulitis prevention begins with proper hygiene. Promptly clean and cover cuts, moisturize dry skin, and avoid scratching. It is important to manage any underlying skin conditions such as eczema or dermatitis and regularly address skin issues with your dermatologist.
Cellulitis FAQs
Your dermatologist can often diagnose cellulitis through a visual examination of the affected area. In some cases, additional tests, such as blood cultures or imaging studies, may be ordered to determine the specific bacteria causing the infection and to assess the extent of the infection.
While cellulitis can be effectively treated with antibiotics, there is a risk of recurrence, especially in individuals with predisposing factors. To reduce the risk of cellulitis recurrence, it's important to practice good skin hygiene, promptly treat any skin injuries or conditions, and manage underlying health issues.
If not treated promptly, cellulitis can lead to various complications, including:
- Abscess formation: Pockets of pus may develop within the affected area.
- Cellulitis recurrence: Some individuals may experience recurrent episodes of cellulitis.
- Lymphangitis: Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, causing red streaks extending from the infected area.
- Systemic infection: Severe cases of cellulitis can lead to a systemic infection, potentially causing sepsis.
- In rare instances, cellulitis may lead to chronic conditions or complications that affect the skin and underlying tissues. \
Seeking early medical attention is crucial to prevent the progression of cellulitis and reduce the risk of complications.
Yes, cellulitis has the potential to spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. The infection typically starts in a localized area but can progress and extend to surrounding tissues. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms of cellulitis are observed, as early treatment with antibiotics can help prevent the spread of the infection.
No, cellulitis itself is not contagious. It is caused by bacteria that commonly reside on the skin's surface or in the environment. However, if the bacteria enter through a wound, it can cause an infection in that specific individual. It cannot be transmitted through casual contact or the air from one person to another.
Yes, eczema can make the skin more susceptible to developing cellulitis. Eczema is a chronic skin condition characterized by dryness, inflammation, and a compromised skin barrier. The compromised skin barrier in eczematous areas allows bacteria, including the types that cause cellulitis, to more easily enter the skin, increasing the risk of developing infections like cellulitis.
The skin affected by eczema is often dry, cracked, and prone to itching, which can lead to scratching. Scratching can further damage the skin barrier, creating openings for bacteria to enter and cause infections. When bacteria penetrate these compromised areas, it can result in cellulitis, which is characterized by redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area.
Due to the weakened skin barrier in eczema, individuals with this condition are more vulnerable to bacterial infections like cellulitis. Therefore, it's crucial for people with eczema to maintain good skincare practices, including keeping the skin well-moisturized, avoiding irritants, and promptly treating any breaks in the skin to reduce the risk of infections, including cellulitis. Consulting with a dermatologist for proper management of eczema and guidance on preventive measures can also be beneficial in reducing the likelihood of skin infections.
Managing Your Eczema Symptoms
Cellulitis Treatments
Featured Blogs
- General Dermatology
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Eczema, a chronic skin condition characterized by inflammation and intense itching, can be challenging to manage, especially during flare-ups.
Read More
- General Dermatology
- Sun Safety
While the sun brings happiness, it poses a significant threat to our skin.
Read More
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
- Chronic Skin Conditions
Explore our comprehensive guide to gain insights into accurate diagnosis and expert care for chronic skin conditions.
Read MoreFeatured Products
Check your local office for current stock!
Check your local office for current stock!


