Curettage
EXAMPLES OF CURETTAGE
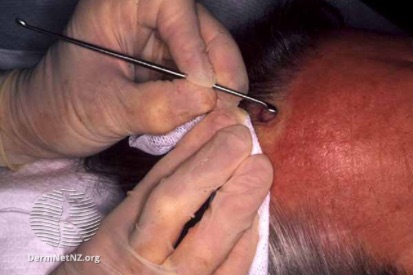
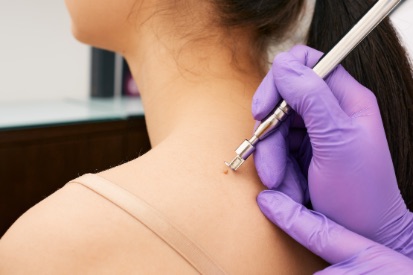

Curettage Explained
It may be used to remove benign growths such as warts or cysts or as part of a biopsy procedure to investigate suspicious or potentially cancerous skin lesions. The procedure is considered minimally invasive and is commonly performed on an outpatient basis. Dermatologists utilize curettage as a versatile tool for both diagnosing and treating a range of skin issues.
Benefits of Curettage
- Benign Lesion Removal: Effectively removes benign skin issues like warts and cysts for cosmetic improvement.
- Diagnostic Tool: Provides a sample for accurate diagnosis, aiding in identifying skin conditions.
- Skin Cancer Treatment: Minimally invasive option for superficial skin cancers, offering simplicity and effectiveness resulting in minimal scarring.
- Outpatient Convenience: Typically performed on an outpatient basis, curettage allows for a swift return home with minimal downtime.
How a Board-certified Dermatologist Can Help?
In cases of suspicious or potentially cancerous lesions, dermatologists may perform curettage as part of a biopsy procedure, providing a sample for laboratory analysis. Additionally, curettage can be employed as a treatment option for certain superficial skin cancers.
Curettage FAQs
Curettage means the removal of tissue or growth by scooping or scraping with a curette tool. This special technique is typically used to remove cancerous and non-cancerous lesions.
Anesthesia is administered before the procedure to minimize/avoid any pain and discomfort.
What to Expect at Your Curettage Appointment
The Curettage process involves using a spoon-shaped instrument to scrape away the targeted skin lesion, with attention to complete removal. After the procedure, wound care instructions and any necessary dressing will be provided. You'll receive post-treatment guidelines, including activities to avoid and skincare routines.
How to Prepare for a Curettage
Planning for Recovery after Curettage
After the curettage procedure, your provider will put a dressing on the area. It’s important that this dressing stays on for 24 hours following the procedure and that it does not get wet.
After 24 hours, it’s time to change the dressing. First, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. Then, remove the old dressing and gently wash the site with soap and warm water. It’s crucial that you do not scrub or scratch the site. Next, pat the area dry, cover it with a thick ointment, and apply a bandage.
During your curettage recovery period, make sure to not submerge the area until the site is completely healed. Furthermore, avoid taking blood thinners, as the area may occasionally bleed after you leave the clinic.
Featured Blogs
- Skin Cancer
- Skin Exams
Total Body Skin Exams (TBSEs) are crucial for healthy skin. Learn more about the importance of TBSEs and skin cancer detection.
Read More
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Learn more about how to spot melanoma and what you can do to keep your skin healthy.
Read More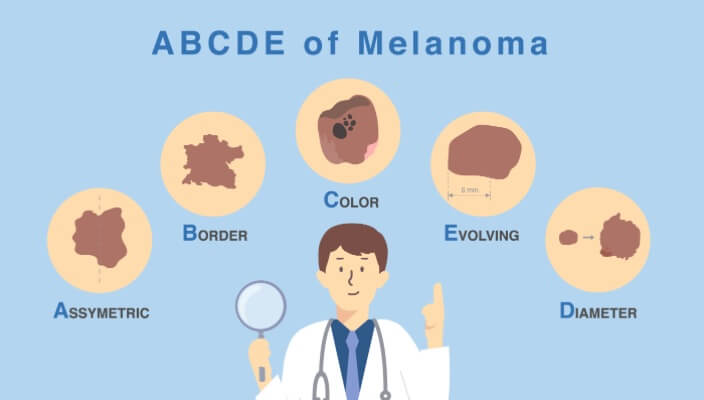
- Skin Cancer
- General Dermatology
- Skin Exams
Learn the ABCDEs of Melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
Read MoreFeatured Products for curettage

Avene Cicalfate+ Restorative Protective Cream 1.3 oz
Rich, nourishing cream infused with postbiotic restorative ingredient, helps protect skin from external aggressors while maintaining proper hydration for optimal skin restoration. Safe for infants, children and adults 1.3 fl oz
iS Clinical Pro Heal Serum Advance+
Pro-Heal Serum Advance+ features our scientifically advanced L-Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C), combined with a superior form of Olive Leaf Extract and pure Vitamins E and A. This powerful formulation significantly increases antioxidant protection while helping improve the appearance of compromised, blemish-prone, and aging skin. 30 mL e 1 fl. oz.


